Most people don’t know about IP addresses, despite the fact that they are an important component of how the Internet works.
This is due to the fact that most of the IP address usage happens in the background. The average user should never have to consider the arrangement of letters and numbers. However, for network, device, and internet processes to work efficiently, they are required.
One of the most important things to understand is the different types of IP Addresses and how they communicate with each other if you want to understand the fundamentals of how IP addresses work.
What Is An IP Address?

Knowing what an IP address is from the beginning is the first step to understanding the many forms of IP addresses. “The set of rules that define the format of data sent over the Internet or another network” is known as an internet protocol or IP.
In other words, it serves as the fundamental building block for how the internet works and how different devices communicate with each other. Since it serves as a unique identifier for each device connected to the network, the IP address is important to this process. There must be a means for computers, routers, and websites to be distinguished on the internet. It does this via IP addresses.
Most products with IP addresses also have simpler names that are easy for people to understand and remember. The nickname “Suzy’s Mac” or “Joe’s Android” may be what you have given to your computer or smartphone. However, all the devices involved will recognize it by the exact IP address it has at that time when it connects to your router or a certain website on the internet.
The Different Types of IP Addresses Categories

There are more than two distinct IP address kinds. Actually, there are a lot of different categories with a few different kinds of IP addresses included in each. Seems challenging, doesn’t it?
When it is explained in simple terms, it is not that difficult to comprehend.
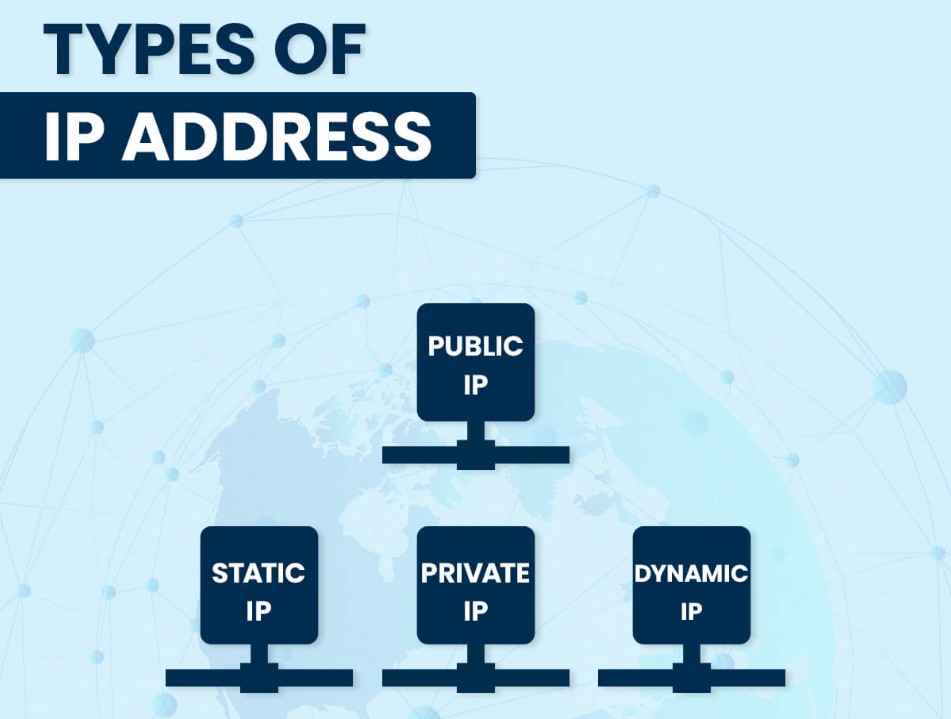
The Different Types of IP Addresses Consumers Have
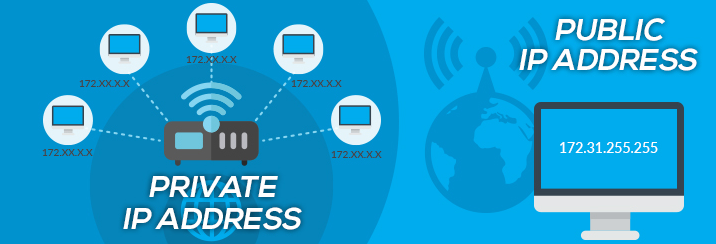
Public IP
The only primary address connected to the entire network is your public IP address. The primary public IP address for your network includes all connected devices, even if each device has its own IP address.
Your internet service provider grants your router access to your public IP address (ISP). They usually have a sizable pool of IP addresses that they have acquired and divided among their various clients. All hardware outside of your internet network will use this address to identify your network and everything associated with it. This is also the site you would visit if you had clicked the link we provided to HostGator to find your IP address earlier.
All your online activity is connected to your public IP address. ISPs can identify which client is responsible for any illegal behavior on their system by looking at the public IP address. So, if you download content without permission or send spam-like emails, your public IP address will be used to identify you.
Private IP
A private IP address is assigned to any device that connects to your home internet network. At your home, any laptops, smartphones, and tablets will clearly be included. However, it also probably includes any Bluetooth gadgets you use, such as speakers or printers, any smart items you’ve set up, any smart TVs or Rokus you may have, and so on. You are more likely to have private IP addresses in your own home as the market for internet of things (IoT) equipment expands.
Each of these items needs to be able to be recognized separately by your router, and many of them also need to be able to recognize one another. For instance, you need the devices to identify one another when you try to pair your Bluetooth headphones with your smartphone. As a result, your router generates private IP addresses, which serve as distinctive network identities for each product.
If you wish to alter your IP address on most devices, there are usually ways to do it as well. You may also find out what the private IP is for the majority of the devices on your network. Yet, you won’t typically need to be aware of each item’s secret IP address. Your router will use that information, but the majority of the routing devices linked to your network interface will have names that are easier to remember whenever you need to locate them. These names may have been provided by you or the device’s manufacturer.
The Different 2 Types of Public IP Addresses
Static IP
Static IP addresses are trusted. You can rely on it to stay the same over the course of months and years as a network is only provisioned once. While not many individuals or businesses require a static IP address, there are some uncommon use scenarios where choosing a static IP address is critical. The main one is for any company that intends to operate its own server.
Static IP addresses will ensure that any website or email addresses on your server will be associated with fixed IP addresses if you manage them yourself. This is important if you want other devices to constantly be able to locate them online.
However, having your own server makes no sense for the majority of people and businesses. Going with a web hosting company that already has a large number of servers and has the necessary resources to manage them safely and properly is much easier and more economical.
Dynamic IP
IP addresses that are dynamic automatically change regularly. A dynamic IP will often be given to internet customers by their ISP. ISPs purchase a big block of IP addresses and instantly allot one to each client. The older one will then be placed back in the pool to be recycled for a different consumer on a periodic basis.
That might seem like an odd way to distribute IP numbers, but it ends up saving ISPs money and making basic maintenance simpler. Nothing unusual needs to be done to re-set up an IP address for a customer once they relocate if the transfer of IP addresses between networks is a frequent and routine operation.
Also, it makes customers feel safer. It becomes considerably more difficult for outsiders to hack into your network interface when your IP address changes frequently. A dynamic address makes the most sense for the majority of internet users, but there are certain exceptions.
The Different 2 Types of Website IP Addresses
Dedicated IP
A dedicated IP address (or several) may be provided with some types of web hosting, while in other cases you may add one as an add-on to your existing plan. at his own. Dedicated IP hosting has a number of other advantages besides helping you avoid potential reverse listings caused by unruly behavior on your server.
One benefit is that you can access your website without using a domain name by entering the IP address. This is useful if you want to start developing and testing your website before registering a domain. While waiting for domain transfer, you can still access your website thanks to this. These are somewhat specialized needs, although they can be advantageous in certain situations.
In addition, it can simplify the use of SSL certificates for your website. Previously, using an SSL certificate required a dedicated IP address. Thankfully, that is no longer the case. If your web hosting provider supports Server Name Recognition (SNI), sites with shared IPs can still purchase SSL. However, using an SSL certificate can be a bit simpler if you have a dedicated IP address.
Finally, you can operate your own FTP server if you have a dedicated IP address. This can facilitate file sharing and transfer between multiple individuals within the company and provides options such as enabling anonymous FTP sharing.
Shared IP
The most popular hosting plans are chosen by website owners who share servers with other websites. Your site will likely be one of the dozens, if not hundreds, of sites hosted on the same server with shared hosting plans—the most popular and affordable option.
That works well for many sites, especially for personal and small business sites that don’t currently get a lot of traffic or have a lot of content. However, it usually indicates that your site is missing a unique, distinct IP address. Instead, one is shared with other sites.
Although it rarely happens, there are some cases where it can happen. For example, if someone uses the IP address shared by your website to engage in illegal activities online, your site may be blacklisted. Some users may lose access to blacklisted sites, and emails sent from your domain may be found in the spam folder. When your site uses a shared IP address, the chance of a problem isn’t high, but it’s still possible.
Conclusion
You won’t need to worry much about IP addresses if you often browse the internet or create websites. Yet gaining information has always been beneficial.
Now that you’ve finished reading this article, you can congratulate yourself on your superior knowledge of IP addresses compared to the majority of internet users.